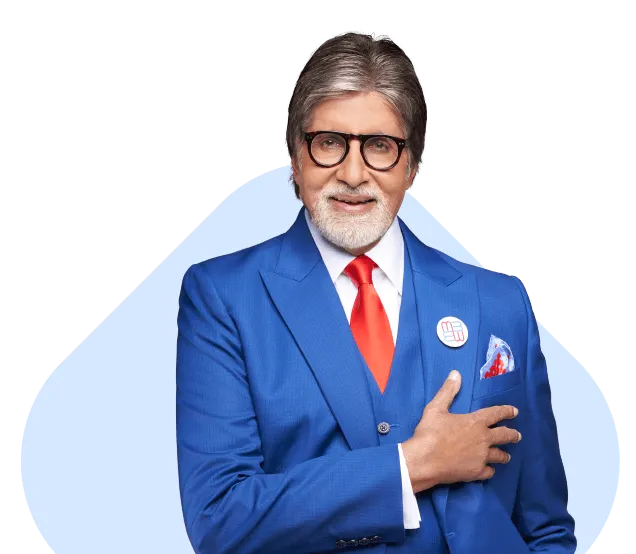
Bladder Stones
Discover advanced Bladder Stones surgery solutions to relieve pain and restore comfort. Our expert team specializes in minimally invasive procedures, ensuring effective treatment for corns and related foot conditions to improve your quality of life.

30k+
Surgeries Done
50k+
Departments Treated
150k+
Conditions Treated
3k+
Specialist Doctors
200+
Cities
Overview of Bladder Stones
Bladder stones, also known as urinary calculi, are solid masses formed from minerals in the urine that accumulate in the bladder. These stones can vary in size, from tiny stones that may be passed without causing symptoms to larger stones that can lead to significant discomfort and complications. The formation of bladder stones typically occurs when urine is retained in the bladder for an extended period. When urine sits in the bladder for too long, minerals in the urine can crystallize and harden, gradually forming stones. This can happen due to various factors, such as urinary tract obstructions, enlarged prostate, urinary retention, or urinary tract infections. Symptoms of bladder stones depend on their size and location within the bladder. Small stones may pass through the urinary system without causing noticeable symptoms. However, larger stones can lead to a range of issues, including: - Abdominal pain or discomfort - Difficulty or pain while urinating - Blood in the urine (hematuria) - Frequent need to urinate - Urinary urgency - Cloudy or foul-smelling urine - Inability to completely empty the bladder Diagnosis of bladder stones typically involves a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examination, and imaging tests such as ultrasound, X-ray, or CT scan. Treatment options for bladder stones may include medications to help dissolve the stones, minimally invasive procedures to remove the stones, or in some cases, surgical intervention. It is essential to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms suggestive of bladder stones to prevent complications and facilitate prompt management.
Why MediBuddy For Health Care

Enhanced Quality of Care
Constant support, a network of premium hospitals and top-tier surgeons.

End-to-End Management
Your only focus should be to go and get your procedure done. Leave the rest to us.

Continuous Guidance
Any problem you may face resolved with one phone call.

Easy financing support
We bring you the best deals, EMI options without compromising on quality
Meet Our Doctors

Dr Praveenkumar T
Urology
25 Years

Dr Sivashankar
Urology
17 Years

Dr Srivathsan R
Urology
16 Years
Diagnosis of Bladder Stones
Diagnosis of Bladder Stones: - A comprehensive diagnosis of bladder stones typically involves several key procedures and tests to accurately identify the condition. - A physical examination by a healthcare provider is often the initial step in diagnosing bladder stones. This may include assessing symptoms and examining the abdomen and pelvic region for signs of tenderness or other abnormalities. - Cystoscopy is a common procedure used to directly visualize the inside of the bladder. During cystoscopy, a thin tube with a camera is inserted through the urethra to examine the bladder walls for the presence of stones or any other issues. - Imaging tests such as CT scans, X-rays, and ultrasound are valuable tools in diagnosing bladder stones. These tests can provide detailed images of the bladder and urinary tract, helping healthcare providers identify the size, location, and number of stones present. - Additionally, a urine test may be conducted to check for abnormalities such as the presence of blood, crystals, or infection. This test can also help in assessing the overall health of the urinary tract and guide treatment decisions. - By combining the results of physical exams, cystoscopy, imaging, and urine tests, healthcare providers can make an accurate diagnosis of bladder stones and develop an appropriate treatment plan tailored to the individual's specific needs.
Treatment Options for Bladder Stones
When it comes to treating bladder stones, there are several important options to consider: - Encouraging Initial Diuresis: While it may seem logical to encourage increased urine production to flush out the stones, it is important to note that this approach could potentially worsen symptoms rather than alleviate them. Therefore, cautious monitoring and management of diuresis are essential in the treatment of bladder stones. - Discharge Advice: Providing thorough discharge advice is crucial in preventing the recurrence of bladder stones once the underlying causes have been identified. This advice should include instructions on dietary modifications and the importance of maintaining a daily urine output of more than 2 litres. - Patient Education: The relationship between patients and healthcare providers, particularly nurses, plays a critical role in the treatment of bladder stones. Nurses have a unique opportunity to educate patients on appropriate dietary changes and the importance of adequate fluid intake to help prevent the formation of new stones. By following these treatment options and engaging in patient education, healthcare providers can effectively manage bladder stones and reduce the likelihood of recurrence.
Prevention of Bladder Stones
Preventing bladder stones is a crucial aspect of managing urological health. There are several key strategies that can help in reducing the risk of developing bladder stones: 1. Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water is essential for preventing bladder stones. Increased fluid intake helps in diluting urine and reducing the concentration of minerals that can lead to stone formation. 2. Manage Underlying Conditions: Conditions such as an enlarged prostate can increase the risk of bladder stones. Managing these underlying conditions through proper medical care and treatment can help in preventing stone formation. 3. Diet Modification: Modifying your diet to reduce the intake of foods high in oxalates, calcium, and purines can be beneficial in preventing bladder stones. Consult a healthcare provider or a nutritionist to create a diet plan that is tailored to your specific needs. 4. Medications: In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe medications to prevent the formation of bladder stones. It is important to follow the medication regimen as prescribed and attend regular check-ups to monitor progress. 5. Risk Factors: Factors such as age, gender, and certain medical conditions can increase the likelihood of developing bladder stones. Understanding these risk factors and addressing them proactively can help in preventing bladder stone formation. By implementing these preventive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of bladder stone formation and maintain optimal urological health.
Complications of Bladder Stones
Bladder stones can lead to various complications that can affect the urinary system and overall health. These complications may include: - Urinary tract obstruction: Bladder stones can obstruct the flow of urine, leading to difficulty urinating and potential backup of urine in the urinary tract. - Pain: The presence of bladder stones can cause pain in the lower abdomen, pelvis, or during urination. This discomfort may vary in intensity and can impact an individual's quality of life. - Nausea and vomiting: Some individuals with bladder stones may experience symptoms of nausea and vomiting, which can be caused by the presence of the stones irritating the bladder or surrounding tissues. - Sepsis: In severe cases, bladder stones can contribute to the development of sepsis, a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by a systemic infection. Sepsis can arise if the stones lead to urinary tract infections that spread to the bloodstream. These complications highlight the importance of early detection and management of bladder stones to prevent adverse outcomes and promote urinary health.
FAQ
What are the common symptoms of bladder stones?
Common symptoms of bladder stones include abdominal pain or discomfort, difficulty or pain while urinating, blood in the urine, frequent need to urinate, urinary urgency, cloudy or foul-smelling urine, and inability to completely empty the bladder.
How are bladder stones diagnosed?
What are the causes of bladder stones?
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy