Lipoma
Discover advanced Lipoma surgery solutions to relieve pain and restore comfort. Our expert team specializes in minimally invasive procedures, ensuring effective treatment for corns and related foot conditions to improve your quality of life.
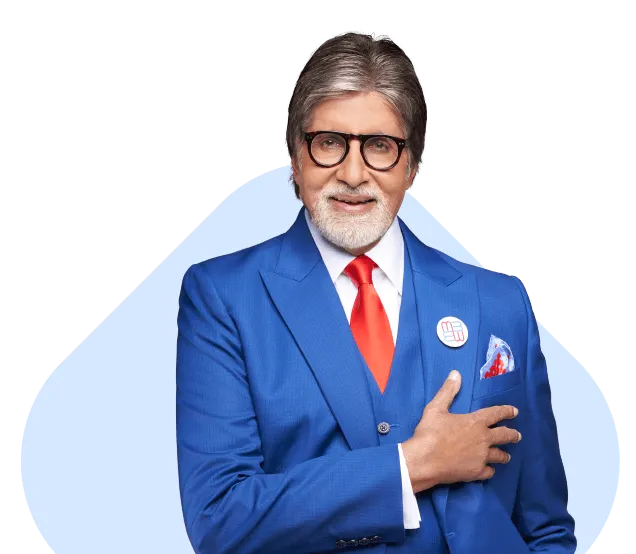

30k+
Surgeries Done
50k+
Departments Treated
150k+
Conditions Treated
3k+
Specialist Doctors
200+
Cities
Lipoma Introduction
Lipomas are benign tumors made up of fat cells that typically develop just below the skin. The exact cause of lipomas is unknown, but individuals with a family history of lipomas have a higher risk of developing them. Furthermore, there are certain conditions, such as Gardner syndrome, Adiposis dolorosa, Madelung disease, and Familial multiple lipomatosis, that are linked to the growth of lipomas. These conditions may predispose individuals to the formation of lipomas in various parts of their body.



Why MediBuddy For Health Care

Enhanced Quality of Care
Constant support, a network of premium hospitals and top-tier surgeons.

End-to-End Management
Your only focus should be to go and get your procedure done. Leave the rest to us.

Continuous Guidance
Any problem you may face resolved with one phone call.

Easy financing support
We bring you the best deals, EMI options without compromising on quality
Meet Our Doctors

Dr Vihrut Bharti
Opthalmology
8 years Experience

Dr Vihrut Bharti
Opthalmology
8 years Experience

Dr Vihrut Bharti
Opthalmology
8 years Experience
Types Of Lipoma
Types of Lipoma: Lipomas, which are benign tumors made up of fatty tissue, can vary in terms of their location and presentation. There are several different types of lipomas based on their specific characteristics and features. These types may include: 1. Superficial subcutaneous lipomas: These are the most common type of lipomas, occurring just beneath the skin's surface. They are typically soft to the touch and easily movable. 2. Deep intramuscular lipomas: These lipomas develop within the muscles and are often firmer in consistency compared to superficial subcutaneous lipomas. They may cause discomfort or pain if they press on surrounding structures. 3. Intermuscular lipomas: Intermuscular lipomas are located between muscles and may grow larger before they are noticed due to their deeper location. 4. Intradermal spindle cell lipomas: These are a rare type of lipoma that tends to occur on the head, neck, or upper trunk. They have a more firm texture compared to other types. 5. Angiolipomas: Angiolipomas contain more blood vessels compared to other lipomas, which may result in a bluish tint to the skin overlying the tumor. They are typically tender to the touch. 6. Hibernomas: Hibernomas are lipomas that consist of brown fat cells and may have a distinct coloration compared to other types of lipomas. They are commonly found in the neck, shoulders, or back. 7. Spindle cell lipomas: Spindle cell lipomas are composed of cells that have a slender, elongated appearance under the microscope. They are usually found on the neck, shoulders, or back. Understanding the different types of lipomas can help in accurately diagnosing and managing these benign fatty tumors.
Diagnosis Of Lipoma
Diagnosing a lipoma typically requires a comprehensive approach to ensure an accurate assessment. The following steps are involved in the diagnosis of lipoma: - Medical History: A detailed medical history is taken by the healthcare provider to understand the patient's symptoms, previous medical conditions, and any relevant family history that may contribute to the diagnosis. - Physical Examination: A thorough physical exam is conducted to assess the size, shape, texture, and mobility of the lump or lumps that may indicate a lipoma. - Screening Tests: Depending on the findings from the medical history and physical exam, the healthcare provider may recommend further screening tests such as: - X-rays: To visualize the internal structures and rule out other conditions. - CT scans (Computed Tomography): Provides detailed cross-sectional images to help identify the nature and location of the mass. - MRI scans (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Utilized to obtain detailed images of soft tissues, aiding in the differentiation of lipomas from other types of tumors. - Ultrasounds: To assess the characteristics and composition of the mass through high-frequency sound waves. - Biopsies: In some cases, a biopsy may be performed to extract a small sample of the tissue for examination under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis and rule out liposarcoma, a rare cancer of fatty tissue. The primary objective of the diagnostic process is to accurately identify the nature of the mass, differentiate it from other potential conditions, and confirm the presence of a lipoma while ruling out malignancies such as liposarcoma. This comprehensive approach helps in determining an appropriate treatment plan tailored to the individual's health needs.
Treatment Options For Lipoma
Treatment options for lipomas depend on various factors such as the size, location, and symptoms associated with the growth. In many cases, especially if the lipoma is small and does not cause any symptoms, observation and monitoring may be recommended rather than immediate treatment. However, if the lipoma is causing discomfort, pain, or affecting mobility, treatment options may include: - Surgical Removal: The most common treatment for lipomas is surgical excision. Surgical removal of the lipoma is typically a simple procedure done under local anesthesia in an outpatient setting. The surgeon makes a small incision, removes the lipoma, and closes the incision with sutures. - Liposuction: In cases where the lipoma is large or in a location where surgical removal may be challenging, liposuction can be considered as an alternative treatment. Liposuction involves inserting a thin tube (cannula) through a small incision and suctioning out the fatty tissue of the lipoma. - Steroid Injections: Steroid injections may be used as a non-surgical treatment option for lipomas. Injecting steroids into the lipoma can help reduce inflammation and shrink the size of the growth. However, multiple injections may be needed for visible results. - Lipoma Injections: Another non-surgical option is injecting lipolysis solutions into the lipoma. These solutions break down the fat cells within the lipoma, leading to its gradual reduction in size over time. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider or a dermatologist to determine the most appropriate treatment option based on individual circumstances. Patients should also be aware that recurrence of lipomas is possible even after successful treatment, and regular follow-ups may be advised to monitor any new growths or changes in existing lipomas.
Surgical Removal Of Lipoma
Surgical removal of Lipoma: - Procedure Overview: - A doctor can often remove a lipoma surgically by making a small incision in the skin and then squeezing out the lipoma. - Local anesthesia is typically administered during the procedure. - Patients undergoing this procedure usually can return home on the same day. - For larger lipomas, a doctor may need to make a more significant incision for complete removal. - In some cases, liposuction can also be used to remove certain lipomas. - Complications: - Complications of lipoma surgical removal may include: - Obstructive symptoms - Bleeding - Nerve compression - Embolism in specific locations - It is essential for the patient to discuss the surgical procedure, potential risks, and follow-up care with their healthcare provider before undergoing surgical removal of a lipoma.
FAQ
What are lipomas?
Lipomas are benign tumors made up of fat cells that typically develop just below the skin.
What are the types of lipomas based on their characteristics?
How are lipomas diagnosed?
What are the treatment options for lipomas?
What is the surgical removal procedure for lipomas?